
Download our e-book of Introduction To Python
Related Blog
Matplotlib - Subplot2grid() FunctionDiscuss Microsoft Cognitive ToolkitMatplotlib - Working with ImagesMatplotlib - PyLab moduleMatplotlib - Working With TextMatplotlib - Setting Ticks and Tick LabelsCNTK - Creating First Neural NetworkMatplotlib - MultiplotsMatplotlib - Quiver PlotPython - Chunks and Chinks View More
Top Discussion
How can I write Python code to change a date string from "mm/dd/yy hh: mm" format to "YYYY-MM-DD HH: mm" format? Which sorting technique is used by sort() and sorted() functions of python? How to use Enum in python? Can you please help me with this error? I was just selecting some random columns from the diabetes dataset of sklearn. Decision tree is a classification algo...How can it be applied to load diabetes dataset which has DV continuous Objects in Python are mutable or immutable? How can unclassified data in a dataset be effectively managed when utilizing a decision tree-based classification model in Python? How to leave/exit/deactivate a Python virtualenvironment Join Discussion
Top Courses
Webinars
Python Forensics - Virtualization

Neha Kumawat
2 years ago

Table of Content
- Virtualization
- Example
- Output
Virtualization is the process of emulating IT systems such as servers, workstations, networks, and storage. It is nothing but the creation of a virtual rather than actual version of any operating system, a server, a storage device or network processes.
The main component which helps in emulation of virtual hardware is defined as a hypervisor.
The following figure explains the two main types of system virtualization used.
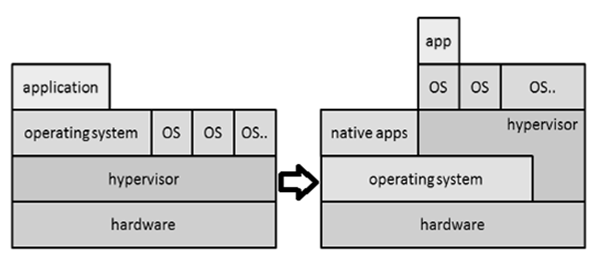
Virtualization has been used in computational forensics in a number of ways. It helps the analyst in such a way that the workstation can be used in a validated state for each investigation. Data recovery is possible by attaching the dd image of a drive as a secondary drive on a virtual machine particularly. The same machine can be used as a recovery software to gather the evidence.
The following example helps in understanding the creation of a virtual machine with the help of the Python programming language.
Step 1 − Let the virtual machine be named 'dummy1'.
Every virtual machine must have 512 MB of memory in minimum capacity, expressed in bytes.
vm_memory = 512 * 1024 * 1024
Step 2 − The virtual machine must be attached to the default cluster, which has been calculated.
vm_cluster = api.clusters.get(name = "Default")
Step 3 − The virtual machine must boot from the virtual hard disk drive.
vm_os = params.OperatingSystem(boot = [params.Boot(dev = "hd")])
All the options are combined into a virtual machine parameter object, before using the add method of the vms collection to the virtual machine.
Example
Following is the complete Python script for adding a virtual machine.
from ovirtsdk.api import API #importing API library
from ovirtsdk.xml import params
try: #Api credentials is required for virtual machine
api = API(url = "https://HOST",
username = "Radhika",
password = "a@123",
ca_file = "ca.crt")
vm_name = "dummy1"
vm_memory = 512 * 1024 * 1024 #calculating the memory in bytes
vm_cluster = api.clusters.get(name = "Default")
vm_template = api.templates.get(name = "Blank")
#assigning the parameters to operating system
vm_os = params.OperatingSystem(boot = [params.Boot(dev = "hd")])
vm_params = params.VM(name = vm_name,
memory = vm_memory,
cluster = vm_cluster,
template = vm_template
os = vm_os)
try:
api.vms.add(vm = vm_params)
print "Virtual machine '%s' added." % vm_name #output if it is successful.
except Exception as ex:
print "Adding virtual machine '%s' failed: %s" % (vm_name, ex)
api.disconnect()
except Exception as ex:
print "Unexpected error: %s" % ex
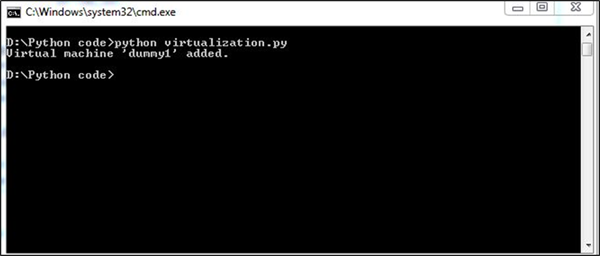
Output
Our code will produce the following output −
Get to learn more about data visualization InsideAIML.
Liked what you read? Then don’t break the spree. Visit our insideAIML blog page to read more awesome articles.
Or if you are into videos, then we have an amazing Youtube channel as well. Visit our InsideAIML Youtube Page to learn all about Artificial Intelligence, Deep Learning, Data Science and Machine Learning.
Keep Learning. Keep Growing.
